? 3D Printing & Additive Manufacturing
? Upload your design. Get a functional part. We make it simple.
Whether you need a rapid prototype for testing or a strong, end-use component, our full suite of industrial 3D printing technologies delivers the right balance of speed, precision, and material performance.
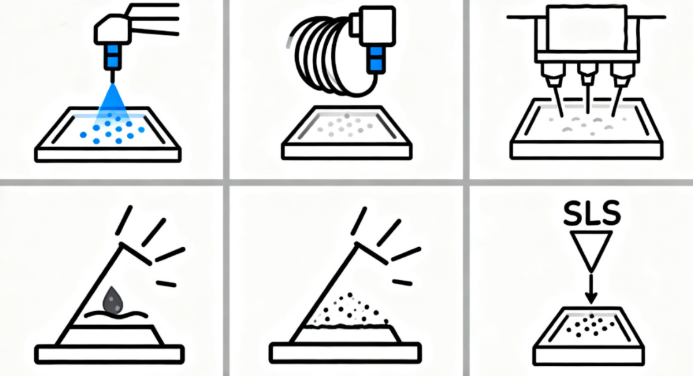
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) 
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Stereolithography SLA
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
? Differentiators
- Match the Technology to Your Need: We don’t force-fit your project. Choose from SLA for ultra-fine details, SLS for strong, complex geometries without supports, FDM with engineering-grade plastics, or Metal SLM for full-density, high-performance parts.
- Engineered Material Library: Your part isn’t generic. We print with the right material for the job—from standard resins and nylons to high-temp PEEK, PPS, and metals like stainless steel and titanium.
- Bridge from Idea to Reality: We support your entire product journey, from initial concept models and functional prototypes to low-volume manufacturing and custom tooling.
- Expertise Built In: Our focus is on manufacturability. We provide practical design feedback (DFAM) to ensure your part prints successfully, performs as intended, and is cost-effective.
? ? 1.Fundamentals of 3D Printing
Core principles, technology comparisons, and getting-started decisions.
- What is 3D Printing? (FDM, SLA, SLS, Metal Printing Explained)
- 3D Printing vs. CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding: How to Choose?
- Understanding the 3D Printing Workflow: From CAD to Part
- The Cost Structure of 3D Printing: A Breakdown
? ?? 2.Design for Additive Manufacturing (DFAM)
DFAM rules to fully leverage the advantages of 3D printing.
- Essential Design Rules for 3D Printing (Overhangs, Wall Thickness, etc.)
- Designing for Support-Free Printing: Angles and Bridges
- Leveraging Lattice Structures for Lightweighting
- Part Consolidation: Combining Assemblies into One Part
- Designing for Different 3D Printing Technologies (FDM vs. SLA vs. SLS)
? ??3. 3D Printing Materials Science
Selecting materials based on technology to balance performance, appearance, and cost.
- 3D Printing Materials Guide: Plastics, Resins, Metals
- FDM Filaments: PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU (Flexible) - Properties and Uses
- SLA Resins: Standard, Engineering, Castable, Dental - A Comparison
- SLS Nylon Powders: PA11, PA12, and Composites
- An Introduction to Metal 3D Printing Materials (Stainless Steel, Titanium, Aluminum)
- How Material Choice Drives Function and Cost
? ??4. Printing Processes & Troubleshooting
Deep dive into technical details and solutions to common printing problems.
- Key Printing Parameters Explained: Layer Height, Infill, Print Speed
- Bed Adhesion Issues: Warping, Elephant Foot - Causes and Fixes
- Solving Print Quality Problems: Stringing, Layer Shifting, Under-Extrusion
- Post-Processing for FDM: Support Removal, Sanding, Smoothing
- Curing and Finishing for SLA/DLP Resin Prints
? ?5. Post-Processing & Surface Finishing
From a raw printed part to a professional finished product.
- 3D Printing Post-Processing Options Overview
- Support Removal and Surface Smoothing Techniques (Sanding, Vapor Smoothing)
- Priming and Painting 3D Printed Parts for a Professional Finish
- Metal Plating and Electroplating on 3D Prints
- Achieving Functional and Aesthetic Finishes for End-Use Parts
? ??6. Quality, Standards & Applications
Ensuring prints meet requirements and exploring industry applications.
- Quality Considerations in 3D Printing: Accuracy, Resolution, Anisotropy
- Common 3D Printing Standards and Certifications (e.g., for Aerospace, Medical)
Application Areas:
- Rapid Prototyping and Functional Testing
- Custom Medical Devices and Surgical Guides
- Lightweight Aerospace and Automotive Components
- Custom Consumer Products and Jewelry
- Tooling, Jigs, and Fixtures (Manufacturing Aids)